Unable to load asset Flutter – Assets are static files included in the compiled Flutter app and available at runtime. Images, fonts, movies, sounds, and other media are just few examples of the many file kinds that can make up these assets.
Flutter “Unable to Load Asset” Error: What You Need to Know
If an image, font, or JSON file in the application bundle cannot be loaded, the “Unable to Load Asset Flutter” error will appear when working with Flutter. The error message appears in the console and typically reads as follows:
[ERROR:flutter/lib/ui/ui_dart_state.cc(199)] Unhandled Exception: Unable to load asset: assets/images/my_image.png
This error occurs when the application is unable to locate the asset file in the specified directory. There can be multiple reasons why the asset file is not being found, including incorrect file path, incorrect file name, or incorrect directory structure.
Reasons Why You Might Get the “Unable to Load Asset” Message
There are a number of potential causes for the “Unable to Load Asset” error in a Flutter app. Following are some examples of frequent triggers:
- Incorrect file path: The code asset file path does not correspond to the file’s actual location.
- Incorrect file name: The code designation for the asset file’s name does not correspond to the file’s actual name.
- Incorrect directory structure: Incorrect directory structure for storing the asset file, as required by the pubspec.yaml.
- File permission issues: The asset file is inaccessible to the program because it lacks the proper permissions.
To update a Flutter project with new assets, the “pubspec.yaml” file must be edited. This file is a configuration file that details the project’s resources and requirements.
How to Fix the “Unable to Load Asset Flutter” Error
Solutions to fix the “Unable to Load Asset flutter” error in your Flutter apps:
- Check the file path: Verify that the code’s reference to an asset file’s path corresponds to the file’s actual location. Be sure to specify the full path to the subdirectory if the file is located there.
- Check the file name: Verify that the asset filename used in the code is the same as the filename used in the asset. Put the file’s extension right after the name if it has one.
- Check the directory structure: Observe the directory structure defined in the pubspec.yaml file to ensure the asset file is located there. File paths in the code and the pubspec.yaml file must be identical.
- Check file permission issues:The asset file must be accessible to the application. Make sure the application can access the external file.
- Run “flutter clean”: Caching issues can cause “Unable to Load Asset Flutter” errors. “Flutter clean” fixes this.
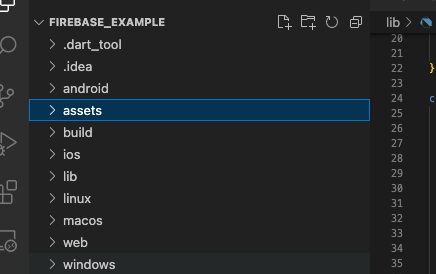
If you still get Unable to Load Asset Flutter, there are several possible reasons and solutions:
- Verify the “pubspec.yaml” file contains accurate asset declarations. Make sure the paths to the assets are relative to the “assets” directory and that the indentation is right.
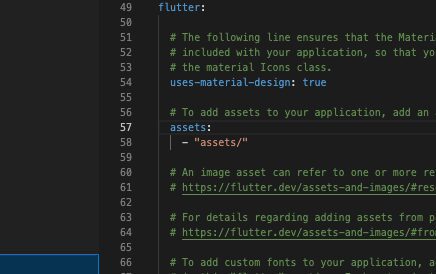
- Check your project’s “assets” directory. If they’re in a subdirectory, include the path in the asset declaration.
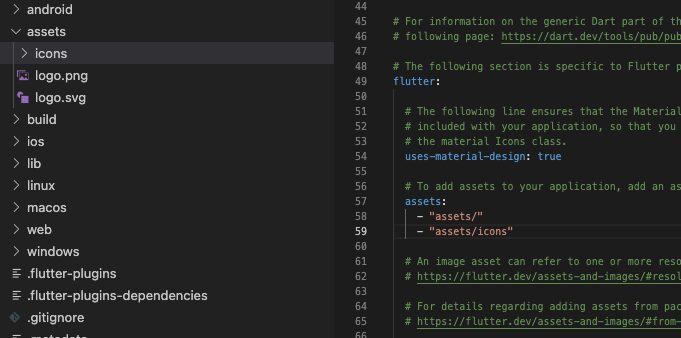
- Check file names and extensions. If you’re loading an image, make sure it’s “.png” or “.jpg.”
- If you are using hot reload, try performing a full restart of the application. Hot reload sometimes does not work correctly with assets and show Unable to Load Asset Flutter.
- To clear the build cache and recompile the project if the asset is not loading properly, type “flutter clean” into the terminal.
- If none of those work, you can always try loading the asset explicitly using the “rootBundle” object. This object, of type “AssetBundle,” has access to methods for Load Asset Flutter in various formats, including bytes, strings, and data streams.
Example how to load an image asset using the rootBundle object in Flutter:
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class MyImageWidget extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return FutureBuilder(
future: loadImageAsset(context, 'assets/images/my_image.png'),
builder: (BuildContext context, AsyncSnapshot snapshot) {
if (snapshot.connectionState == ConnectionState.done) {
return Image(image: snapshot.data);
} else {
return CircularProgressIndicator();
}
},
);
}
Future loadImageAsset(BuildContext context, String assetPath) async {
final ByteData data = await rootBundle.load(assetPath);
final Uint8List bytes = data.buffer.asUint8List();
final ImageProvider imageProvider = MemoryImage(bytes);
return imageProvider;
}
}
The app’s assets/images directory has the my image.png image asset, which is loaded by a widget called MyImageWidget. An Image widget can show a picture by calling the rootBundle object’s loadImageAsset() method, which retrieves the image data and converts it into a MemoryImage object.
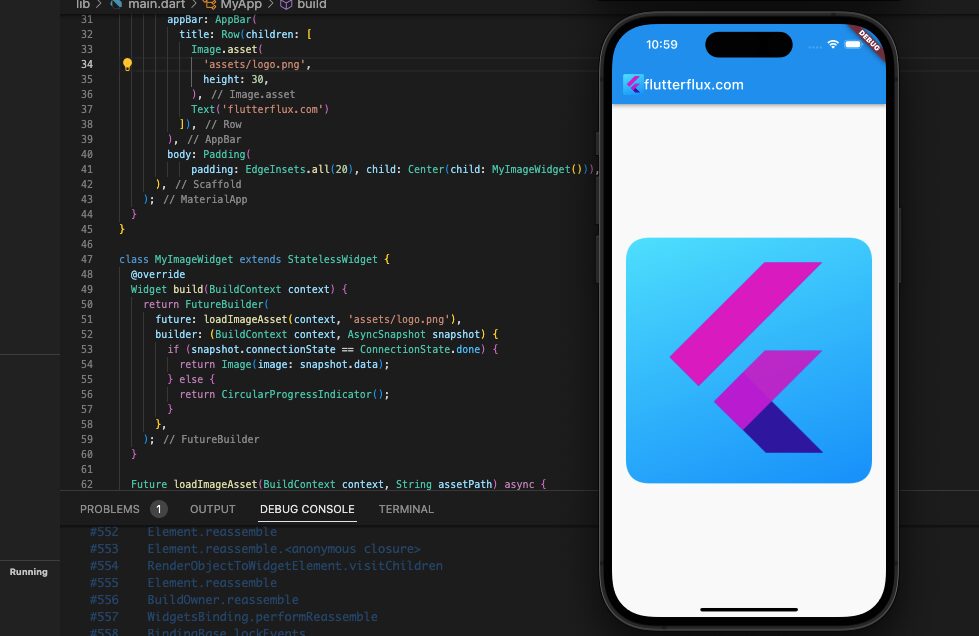
Loading indicators are displayed when images are being loaded while using the FutureBuilder widget. In order to display the image, the Image widget uses the ImageProvider that was returned by the loadImageAsset() method after the image has been loaded. It’s important to remember that setting the Image widget’s width and height or enclosing it in a widget that gives constraints, like a Container or AspectRatio, can help ensure that the ImageProvider is displayed correctly in the Image widget.
If your Flutter app is experiencing problems Load Asset Flutter, try these solutions.
Conclusion
Flutter mobile app developers often encounter the “Unable to Load Asset” error. When an application bundle asset file cannot be loaded, this error occurs. Incorrect file path, name, directory structure, or permissions can cause the error. Developers should check the file path, name, directory structure, file permissions, and run the “flutter clean” command to resolve this error.








